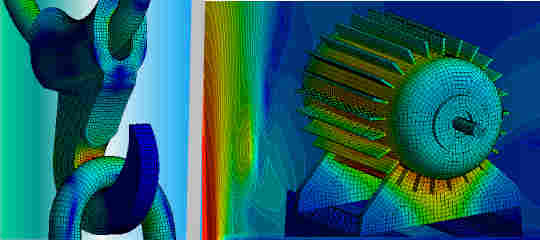
FEA, CFD & Simulation
Stresses in components, temperature fields in machines and devices, vibration modes of structures, fluid flow fields, electromagnetic fields - totally different physical phenomena and mechanisms. Common to all of them is the fact, that they cannot be calculated by classical analytical methods, except in case of very elementary geometries and boundary conditions. It's about continuous systems, i.e. systems with an infinite number of degrees of freedom. In a numerical computation, these systems are discretized, i.e. the degrees of freedom are reduced to a finite number.
The best known method of this kind is the finite element method (FEM) or finite element analysis (FEA) which is widely used for structural computations. Other well-established methods are the finite difference method and the finite volume method. The latter is mainly used in computational fluid dynamics (CFD).
On which numerical method the computation software is based, doesn't matter from the customer's point of view. Much more important, and essential for a successful analysis are other things: An appropriate translation of the real situation into a model including the choice of suitable boundary conditions, and a correct interpretion of the results. Appropriate translation means: as complex as necessary, as simple as possible. This demands carefully weighing up substantial outcome and high precision against computing time and costs. Appropriate modeling and correct interpretation require considerable experience and a good understanding of the relevant laws of physics.
Based on our experience in the application of physical mechanisms and in numerical methods, we can offer you numerical computations in several application fields:
- Structural analyses (stresses, strains, deformations)
- Static, transient and dynamic load cases
- Elastic and plastic deformation
- Heat stresses
- Harmonic and modal analyses
- Thermal analyses - computation of
- temperature fields and heat flows,
- convective heat transfer and radiation,
- static und transient load cases.
- Assessment of stresses
- Fatigue analyses according to the appropriate technical guideline (FKM directive, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)
- Computational fluid dynamics
- Fluid flow through pipes and devices
- Fluid flow around bodies
- Stationary and time-dependent fluid flows
- Multiphase flows and mixture of fluids
- Pipe stress analyses
Numerical computations and simulation have become essential engineering tools in development and design of processes and components. They complement experiments and are replacing more an more expensive test series. For us, they are indispensible ingredients in our toolbox.
For structural and thermal analyses we're using predominantly ANSYS Mechanical, for computational fluid dynamics (CFD) ANSYS Fluent and for pipe stress analyses CEASAR II.
